Fixed Cost Definition
Fixed Cost is the cost or expense that is not affected by any decrease or increase in the number of units produced or sold over a short-term horizon. In other words, it is the type of cost that is not dependent on the business activity but is rather associated with a period.
It can be seen as expenses incurred by a company irrespective of the level of business activity, which may include the number of units produced or sales volume achieved. Fixed cost is one of the two major components of the total cost of production. The other component is the variable cost. Examples are monthly rental paid for accommodation, salary paid to an employee, etc. However, please note that such cost is not permanently fixed but changes over time.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be HyperlinkedFor eg:Source: Fixed Cost (wallstreetmojo.com)
Fixed Cost Formula
We can derive this formula by deducting the product of variable cost per unitVariable Cost Per UnitVariable cost per unit refers to the cost of production of each unit produced, which changes when the output volume or the activity level changes. These are not committed costs as they occur only if there is production in the company.read more of production and the number of units produced from the total cost of production.
Examples
- Leasing office space is a fixed cost. As long the business operates in the same space, the lease or rent cost remains the same.
- Utility bills like heating or cooling as per the season changes are another cost not affected by the change in business operations.
- When a company registers itself on a website domain, a monthly charge is to be paid that remains fixed irrespective of the activities performed on the website.
- When a company registers itself on a website domain, a monthly charge is to be paid that remains fixed irrespective of the activities performed on the website.
- When a company integrates its e-commerce platforms with the website to continue communications and transactions with its customers, there are charges levied for this integration, which are payable monthly.
- When a business starts its operations, then it leases or rents warehouse space whose charge is payable monthly. This charge does not change even if the business decides to store more or fewer products, keeping in mind the storage and capacity limits. This warehouse rent is a fixed cost.
- The equipment purchased to produce the products belongs to the business once purchased, which depreciates over time. Depreciation costs are considered when the company is aware of what time the equipment needs to be replaced every year.
- Companies hire trucks as per their logistics, and leasesLeasesLeasing is an arrangement in which the asset’s right is transferred to another person without transferring the ownership. In simple terms, it means giving the asset on hire or rent. The person who gives the asset is “Lessor,” the person who takes the asset on rent is “Lessee.”read more on trucks are fixed, which do not change depending on the number of shipments the company undertakes.
- If a business does its financing with the help of bank loans, then loan payments remain the same irrespective of the business’s performance. The loan repayment amount is fixed as long as a balance is paid on that loan.
- Health insurance for a business is fixed as the recurring costs to the insurer are fixed.
Step by Step Calculation of Fixed Cost
Example #1
Let us take the example of company ABC Ltd, a toy manufacturing unit. According to the production manager, the number of toys manufactured in April 2019 is 10,000. The total cost of production for that month as per the accounts department stood at $50,000. Calculate the fixed cost of production if the variable cost per unit for ABC Ltd is $3.50.
Solution:
Given,
- Variable cost per unit = $3.50
- Total cost of production = $50,000
- Number of units produced = 10,000
Cost of production of ABC Ltd for April 2019 can be calculated as,
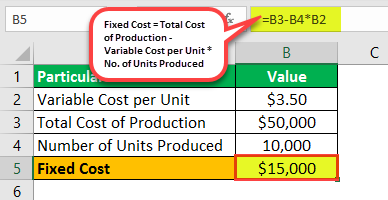
= $50,000 – $3.50 * 10,000
FC = $15,000
Example #2
Let us take another example of company XYZ Ltd, a shoe manufacturing unit. According to the production manager, the production information is available for March 2019 is as follows:
- Raw material cost per unit is $25
- Total number of shoe manufacturer is 1,000
- Labour charge is $35 per hour
- Time taken to produce a shoe is 30 minutes
- The total cost of production is $60,000
Calculate the Fixed Cost of production for XYZ Ltd in March 2019.
Solution:
Given,
- Total cost of production = $60,000
- Raw material cost per unit = $25
- Labor costLabor CostCost of labor is the remuneration paid in the form of wages and salaries to the employees. The allowances are sub-divided broadly into two categories- direct labor involved in the manufacturing process and indirect labor pertaining to all other processes.read more per hour = $35 per hour
- Time taken to produce a unit = 30 min = 30 / 60 hours = 0.50 hours
- Number of units produced = 1,000
So, the calculation of variable cost per unit will be –
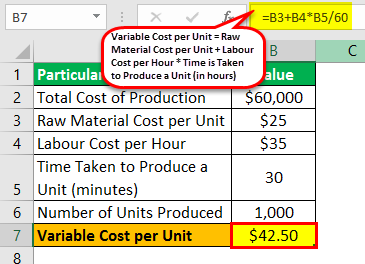
Variable Cost per Unit = $25 + $35 * 0.50
Variable Cost per Unit = $42.50
Therefore, the FC of production of XYZ Ltd for the month of March 2019 can be calculated as,
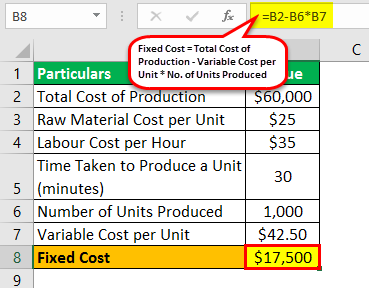
= $60,000 – $42.50 * 1,000
FC = $17,500
Therefore, the FC of production of XYZ Ltd for the month of March 2019 is $17,500.
Please refer given excel template above for detail calculation.
Advantages
- Fixed costs remain at the same level throughout a company’s production process unless any major capital expenditureCapital ExpenditureCapex or Capital Expenditure is the expense of the company’s total purchases of assets during a given period determined by adding the net increase in factory, property, equipment, and depreciation expense during a fiscal year.read more is undertaken. For instance, if a company purchases and installs a machine, post that the company will charge depreciation expense every year irrespective of the level of production.
- It is relatively easier to account for this cost because it does not change in line with the volume of goods produced or sold.
- Although it does not change with an increase in production volume, per-unit fixed cost decreases, which is an encouragement for the production team to produce more;
- Production output and costs typically remain the same for a relevant output range.
- It reduces a company’s net income for the accounting periodAccounting PeriodAccounting Period refers to the period in which all financial transactions are recorded and financial statements are prepared. This might be quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the period for which you want to create the financial statements to be presented to investors so that they can track and compare the company’s overall performance.read more in reduced tax liability, which eventually cascades to cash savings.
- Cost intensive industries act as a barrier to new entrants or eliminate smaller competitors; it discourages new competitors from making an entry into the market.
Disadvantages
- One of the major disadvantages is the surge in per-unit fixed cost if a company fails to operate at a certain minimum production rate. If a company has a large number of such costs, then a fall in production or sales volume can squeeze the profit marginsProfit MarginsProfit Margin is a metric that the management, financial analysts, & investors use to measure the profitability of a business relative to its sales. It is determined as the ratio of Generated Profit Amount to the Generated Revenue Amount. read more.
- It is very tough to find any direct relationship between the product and the fixed cost if the company is into multiple products. As such, at times, the allocation or apportion of costAllocation Or Apportion Of CostCost Allocation is the procedure of recognizing & assigning costs to different cost objects like a product, department, program, customer, etc., as per the cost driver serving as the base for this process. read more is done based on the profitability of each division, which can result in wrong financial productivity measurement.
Conclusion
It can be seen from the above explanations that “fixed cost” is very stable and does not change over some time. However, higher production or sales volume can result in better absorption of fixed costs, resulting in improved profitability. As such, it is important to understand the concept of fixed assets as it can be crucial in achieving profitability targets.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is a Fixed Cost and its definition. Here we discuss how to calculate fixed cost along with its formula and advantages and disadvantages. You can learn more about accounting from following articles –
- Fixed Cost vs Variable Cost
- Variable Costing Definition
- Absorption Costing
- Overhead Costs Calculation



![How to fix error 0xc000000e windows 10 2022 100 SOLVED 11 How to fix error 0xc000000e windows 10 2022: [100% SOLVED]](https://dreamcheeky.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/How-to-fix-error-0xc000000e-windows-10-2022-100-SOLVED.jpg)
![how to fix Error code 0xc0000001 2022 100 FIXED 12 how to fix Error code 0xc0000001 2022 :[100% FIXED]](https://dreamcheeky.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/how-to-fix-Error-code-0xc0000001-2022-100-FIXED.jpg)